Tackling standardization in fluorescence molecular imaging
Abstract
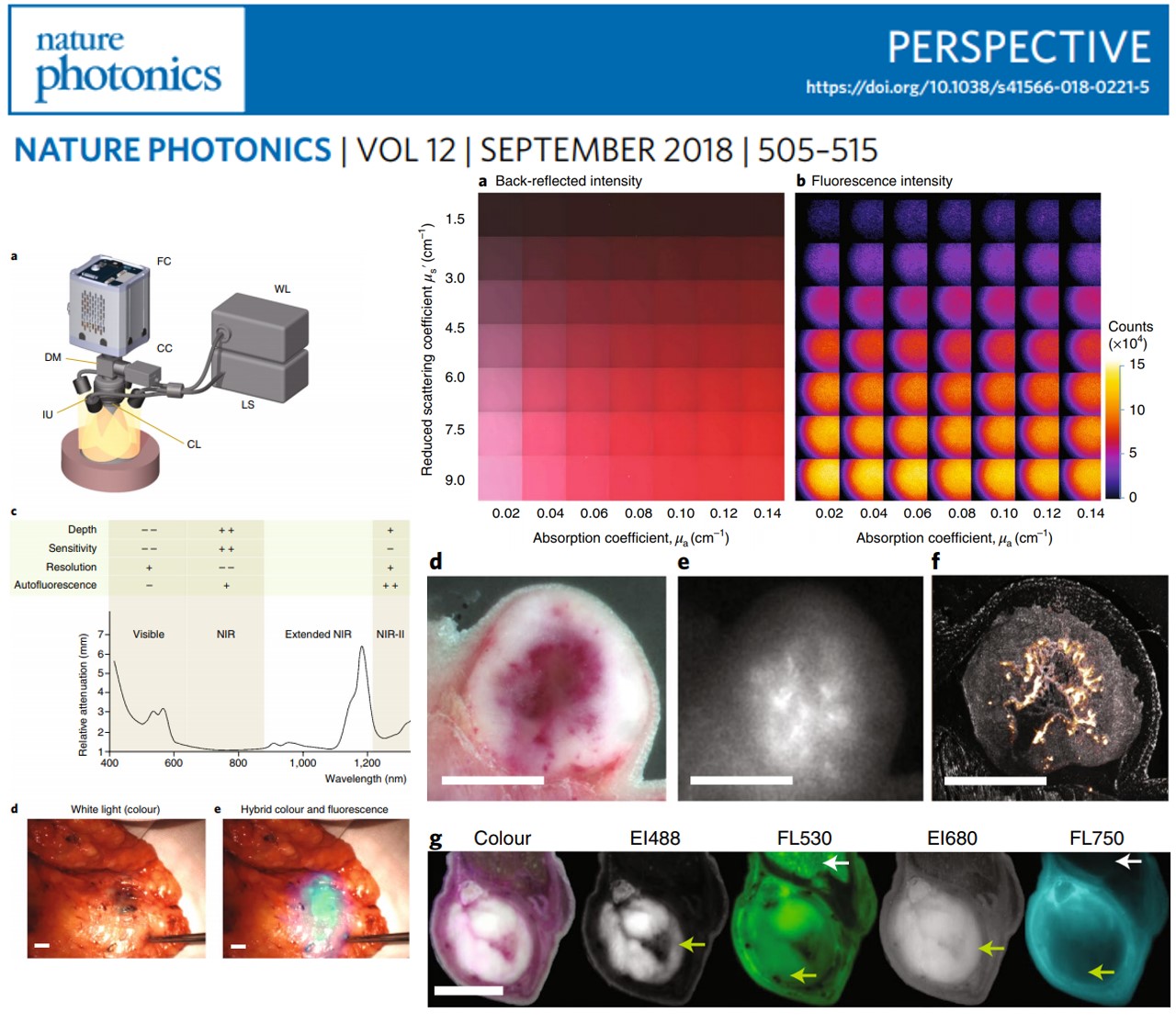
The emerging clinical use of targeted fluorescent agents heralds a shift in intraoperative imaging practices that overcome the limitations of human vision. However, in contrast to established radiological methods, no appropriate performance specifications and standards have been established in fluorescence molecular imaging. Moreover, the dependence of fluorescence signals on many experimental parameters and the use of wavelengths ranging from the visible to short-wave infrared (400–1,700 nm) complicate quality control in fluorescence molecular imaging. Here, we discuss the experimental parameters that critically affect fluorescence molecular imaging accuracy, and introduce the concept of high-fidelity fluorescence imaging as a means for ensuring reliable reproduction of fluorescence biodistribution in tissue.